Solar panels are one of the most effective tools we have for combating climate change. They are non-polluting, their energy source is renewable and inexhaustible, they can be recycled, and every kWh created by solar panels is a kWh not generated in polluting facility plants that emit greenhouse gases.
All of these contributions from solar power plants are important in the fight against climate change, but what exactly is climate change and how does it affect our planet?
Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
There are thousands of planets in the universe, some having features conducive to life, and others that are so hot, cold, or toxic that life as we know it may appear impossible. However, in addition to its excellent position in relation to the Sun, Earth has another feature that distinguishes it from other planets in our galaxy: the presence of the ozone shield.
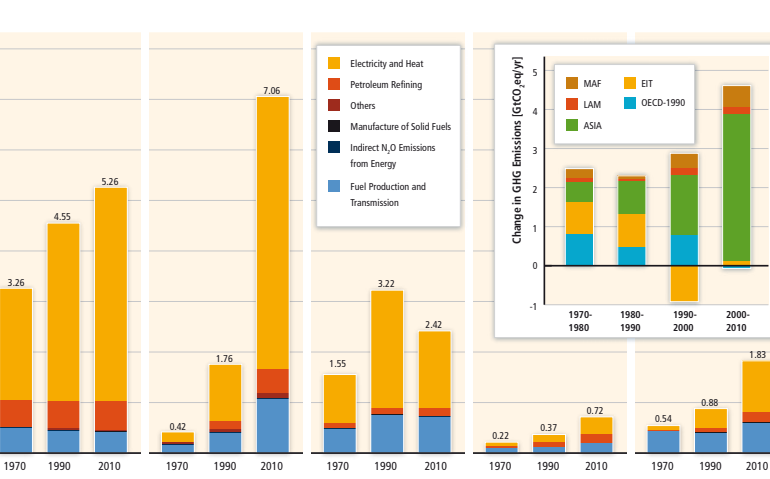
The so-called Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) that make up this ozone layer include water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, chlorofluorocarbons, hydrofluorocarbons, and carbon dioxide (CO2). In the planet’s atmosphere, the accumulation of GHG generates a layer that reflects UV light and concentrates incoming heat from solar energy. This permits planet Earth to maintain temperature ranges that are appropriate for living, which would otherwise be too cold for life to survive.
The Greenhouse Effect is a natural phenomenon that has happened over millions of years. However, raising GHG levels above normal has a detrimental impact on Earth’s temperature since the layer grows thicker than it should be and heat levels rise dramatically, resulting in dangerously high temperatures for the planet.
Our planet’s carbon dioxide levels have fluctuated about 200 parts per million, peaking around 280 parts per million in the past. Carbon dioxide levels, on the other hand, have risen to astronomic levels around 400 parts per million since the industrial revolution. There are a number of probable causes for this drastic change, but scientists agree that human activity is the main reason for the rapid rise in CO2 levels.
According to a 2014 IPCC report, the energy supply sector accounted for about half of all GHG emissions, making it the most significant contributor to global GHG emissions. Despite the Kyoto Protocol, this sector’s GHG emissions increased by 36% between 2000 and 2010, with CO2 emissions from coal (43%), oil (36%), and gas (36%) being the largest sources (20 percent ).
According to the United States Global Change Research Program’s Fourth National Climate Assessment Report published in 2018, if CO2 emissions are not reduced by 45 percent by 2030, a 1.5°C increase in global temperature will be unavoidable. This increase in the global temperature leads to serious consequences for the planet such as rising sea levels, melting ices, droughts, hurricanes, storms, snowfalls, heat waves, etc.
Solar Energy – A Source of Light to Fight Climate Change
Solar panels are one of the key drivers in the reduction of carbon emissions around the world since they are one of the most widely available, affordable, and feasible renewable energy options. The most recent data on the tool is from 2014, but we still have a good notion of how much solar energy contributes to the market.
In the United States, it has been estimated that roughly 17.5 million tons (MT) of CO2 can be avoided, equating to 22,000 GWh of power. China made great contributions as well, releasing 20 MT of CO2 and injecting 25,000 GWh of energy into the system. Germany was the largest donor in that year, avoiding 29 MT and producing over 35,000 GWh. This translates to 18 million tonnes of coal, 3.38 million tonnes of natural gas, and 9 million tonnes of oil. Other countries’ contributions totaled about 80,000 GWh, avoiding 63 MT of CO2 emissions for the environment, including Japan, Italy, Spain, France, the United Kingdom, Australia, India, and South Korea.
These figures have already surpassed the expected estimates, as solar energy continues to rise year after year. As a point of comparison, roughly 177 GW of installed capacity was available in 2014, whereas around 402 GW of installed capacity is accessible globally in 2017. That’s a 130 percent increase over just three years.

Solar Panels for Residential Use
Hiring solar businesses to put solar panels on their houses is one of the best ways that most of us can contribute to the fight against climate change. Solar energy has a number of benefits that may be used to reduce carbon emissions, and going solar for your home will also save you money.
Sunlights and other solar-powered household items all contribute to lowering our carbon footprint. While the reductions are little, every little bit helps, and when done on a wide scale, it can make a significant difference in the long run.